Components¶
The theta package comes with the following modules:
- RTBM (
theta.rtbm) - Model (
theta.model) - Layers (
theta.layers) - Minimizers (
theta.minimizer) - Activations (
theta.activations) - Initializers (
theta.initializers) - Cost functions (
theta.costfunctions) - Stopping conditions (
theta.stopping)
These modules provide all the required components to train Riemann-Theta Boltzmann Machines for probability density estimation, regression and classification.
RTBM¶
The theta.rtbm module contains the definition of class
RTBM. This object provides the simplest interface to the parameters
of the RTBM and to the probability and expectation values.
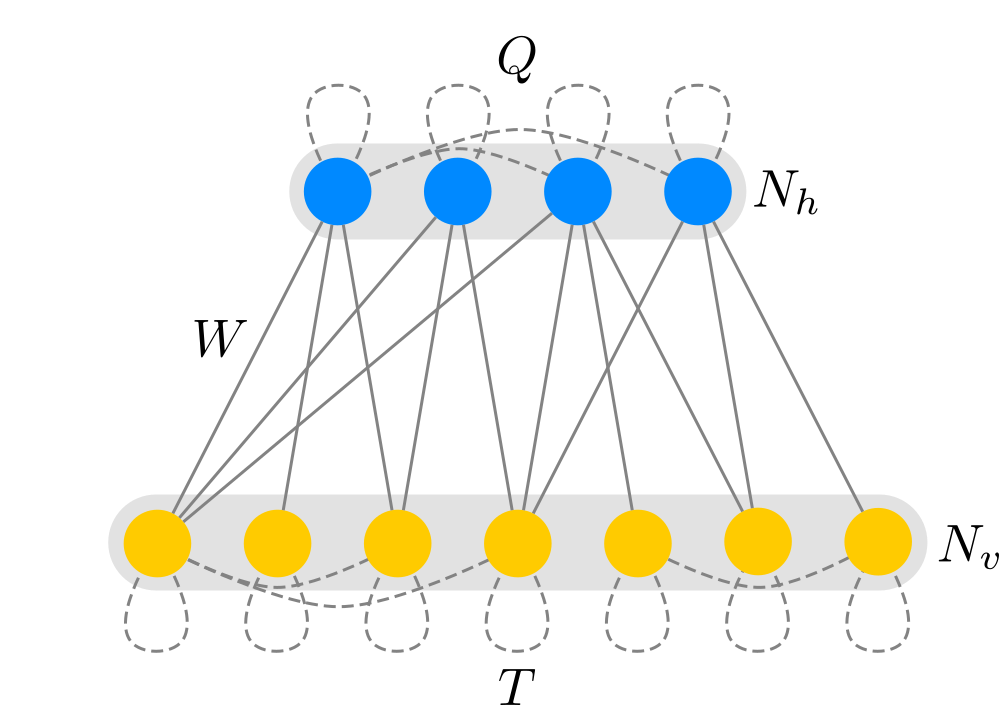
Schematically, the RTBM is given by the network configuration
where \(T\) is the connection matrix of the visible sector with \(N_v\) visible units, \(Q\) of the hidden sector with \(N_h\) hidden units and \(W\) the inter-connections.
-
class
theta.rtbm.RTBM(visible_units, hidden_units, mode=0, init_max_param_bound=2, random_bound=1, phase=1, diagonal_T=False)¶ This class implements the Riemann-Theta Boltzmann Machine.
Parameters: - visible_units (int) – number of visible units.
- hidden_units (int) – number of hidden units.
- mode (theta.rtbm.RTBM.Mode) – set the working mode among: probability mode (
Mode.Probability), log of probability (Mode.LogProbability) and expectation (Mode.Expectation), seetheta.rtbm.RTBM.Mode. - init_max_param_bound (float) – maximum value allowed for all parameters during the CMA-ES minimization.
- random_bound (float) – selects the maximum random value for the Schur complement initialization.
- phase (complex) – number which multiplies w and bh
phase=1for Phase I andphase=1jfor Phase II. - diagonal_T (bool) – force T diagonal, by default T is symmetric.
- check_positivity (bool) – enable positivity condition check in
set_parameters.
Properties (setters and getters):
- mode (theta.rtbm.RTBM.Mode) - sets and returns the RTBM mode.
- bv (numpy.array) - sets and returns the Bv.
- t (numpy.array) - sets and returns the T.
- bh (numpy.array) - sets and returns the Bh.
- w (numpy.array) - sets and returns the W.
- q (numpy.array) - sets and returns the Q.
Example
from theta.rtbm import RTBM m = RTBM(1, 2) # allocates a RTBM with Nv=1 and Nh=2 print(m.size()) # returns the total number of parameters output = m(x) # evaluate prediction
-
predict(x)¶ Performs prediction with the trained model. This method has a shortcut defined by the parenthese operator, i.e.
model.predict(x)andmodel(x)are equivalent.Parameters: x (numpy.array) – input data, shape (Nv, Ndata) Returns: evaluates Model predictions. Return type: numpy.array
-
random_init(bound)¶ Random initializer which satisfies the Schur complement positivity condition. If
diagonal_T=Truethe initial Q and T are diagonal and W is set to zero.Parameters: bound (float) – the maximum value for the random matrix X used by the Schur complement.
-
mean()¶ Computes the first moment estimator (mean).
Returns: the mean of the probability distribution. Return type: float Raises: theta.rtbm.AssertionError– ifmodeis nottheta.rtbm.RTBM.Mode.Probability.
-
size()¶ Returns: the size of the RTBM. Return type: int
-
get_parameters()¶ Returns: flat array with all RTBM parameters. Return type: numpy.array
-
get_gradients()¶ Returns: flat array with calculated gradients [Gbh,Gbv,Gw,Gt,Gq]. Return type: numpy array
-
set_bounds(param_bound)¶ Sets the parameter bound for each parameter.
Parameters: param_bound (float) – the maximum absolute value for parameter variation.
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter for the GA. Return type: list of numpy.array
Model¶
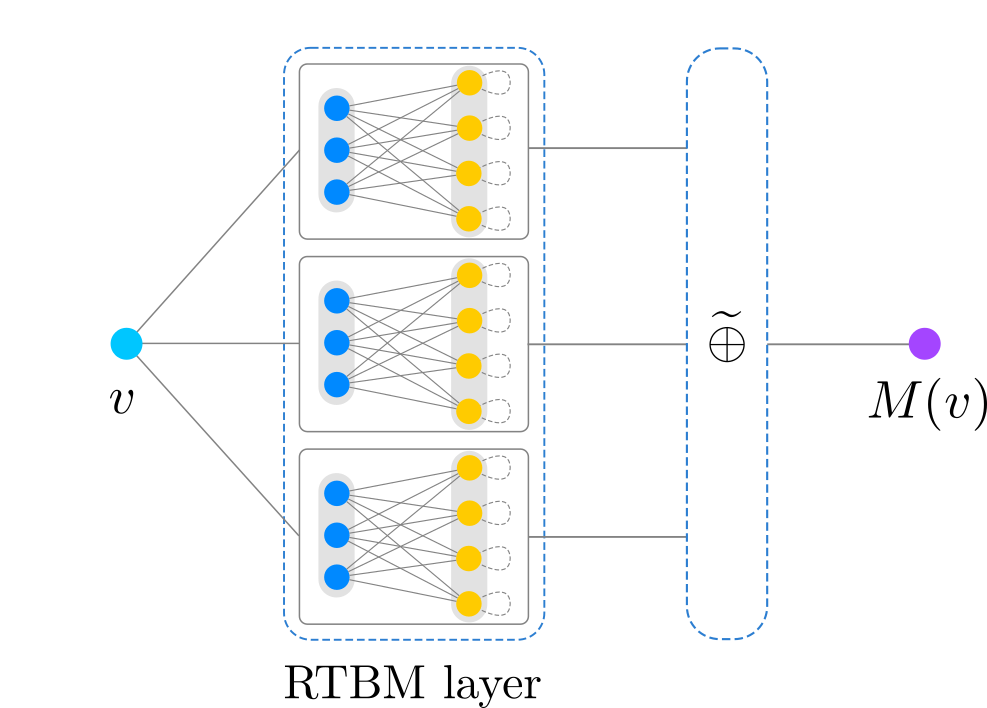
The theta package provide a dedicated container for RTBM probability
mixtures models and theta neural networks (TNNs) through the class
Model stored in theta.model.
This module allows the concatenation of objects for building mixture
model based on multiple RTBMs and a final NormAddLayer, such as:
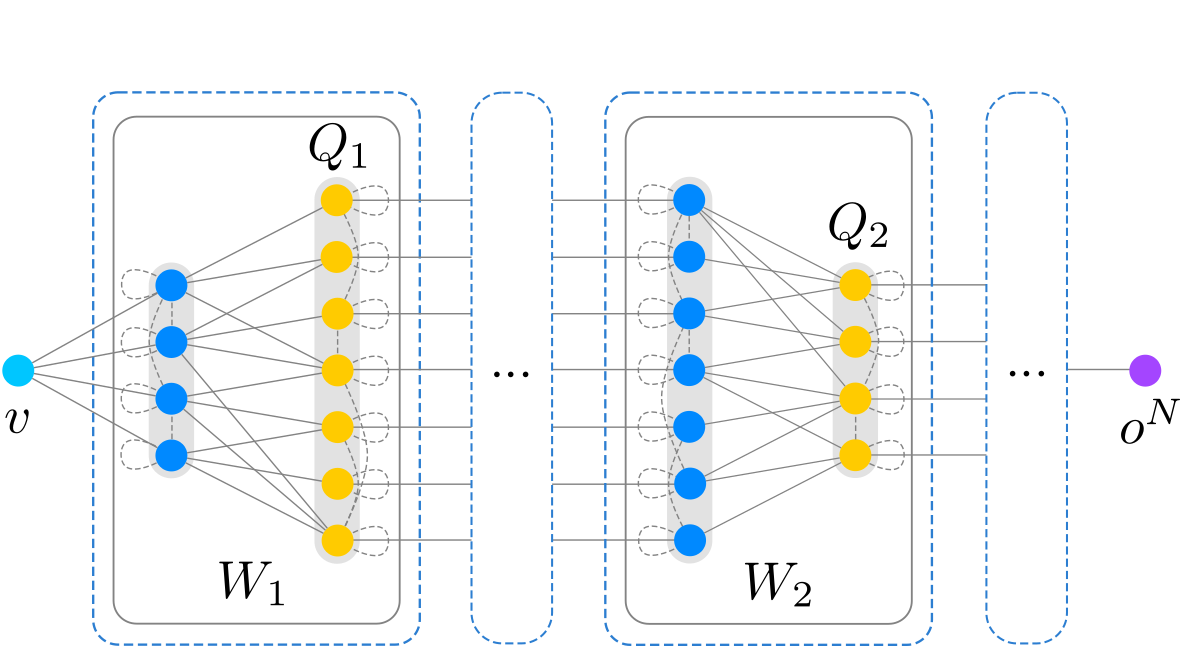
and the possibility to build TNNs, e.g.:
Further information about the implemented layers for the TNNs are listed in the Layers section of this document.
-
class
theta.model.Model¶ The model class which holds layer for building mixture models and theta neural networks.
Example
from theta.theta import Model from theta.layers import ThetaUnitLayer, AddNormLayer m = Model() # allocates a RTBM with Nv=1 and Nh=2 m.add(ThetaUnitLayer(1,2)) m.add(NormAddLayer(2,1))
-
predict(x)¶ Performs prediction with the trained model. This method has a shortcut defined by the parenthese operator, i.e.
model.predict(x)andmodel(x)are equivalent.Parameters: x (numpy.array) – input data, shape (Nv, Ndata) Returns: evaluates Model predictions. Return type: numpy.array
-
add(layer)¶ Add layer to the model instance.
Parameters: layer (theta.layers) – any layer implemented in theta.layers (Layers). Warning
The layer input size must match the output size of previous layer!
-
size()¶ Returns: the size of the RTBM. Return type: int
-
get_parameters()¶ Collects all parameters and returns a flat array.
Returns: flat array with current matrices weights. Return type: numpy.array
-
get_gradients()¶ Collects all gradients and returns a flat array.
Returns: flat array with calculated gradients. Return type: numpy array
-
get_layer(N)¶ Parameters: N (int) – the layer number. Returns: returns the N-th layer stored in the model Return type: theta.layers
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter of all layers. Return type: list of numpy.array
-
gradient_check(g, x, epsilon)¶ Performs numerical check of gth gradient.
Parameters: - g (int) – id of gradient to check.
- x (numpy.array) – input data shape (Ninput, Ndata).
- epsilon (float) – infinitesimal variation of parameter.
Returns: the numerical and analytical gradients.
Return type: floats
-
Layers¶
The theta package implements the following layers:
- Theta Probability Unit: provides a layer with multiple RTBMs setup in probability mode. This layer is used to build probability and mixture models.
- Theta Diagonal Expectation Unit: A layer consisting of a RTBM in expectation mode with diagonal \(Q\). This layer is suitable for regression and classification applications, and can be combined with other layers into a deep model.
- Normalized Additive: performs a weighted sum of the inputs. This layer guarantees a positive and normalized output and is used to build mixture models.
- Linear: a standard linear layer for testing and benchmarking purposes.
- Non-Linear: a non linear layer for testing and benchmarking purposes.
All layers are inherited from the theta.layers.Layer class, so
custom layers can be implemented by extending that class.
Theta Probability Unit¶
-
class
theta.layers.ThetaUnitLayer(Nin, Nout, Nhidden=1, init_max_param_bound=2, random_bound=1, phase=1, diagonal_T=False)¶ Allocate a Theta Unit Layer working in probability mode
Parameters: - Nin (int) – number of input nodes
- Nout (int) – number of output nodes (i.e. # of RTBMs)
- Nhidden (int) – number of hidden layers per RTBM
- init_max_param_bound (float) – maximum bound value for CMA
- random_bound (float) – the maximum value for the random matrix X used by initialization
- phase (complex) – number which multiplies w and bh
phase=1for Phase I andphase=1jfor PhaseII. - diagonal_T (bool) – force T diagonal, by default T is symmetric.
-
get_unit(N)¶ Return the singular RTBM unit.
Parameters: N (int) – the Nth RTBM unit. Returns: the Nth RTBM unit. Return type: theta.rtbm.RTBM
-
get_parameters()¶ Returns: the parameters as a flat array [b,w,q]. Return type: numpy.array
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter of the layer for the GA. Return type: list of numpy.array
-
size()¶ Returns: total number of parameters. Return type: int
-
get_gradients()¶ Returns: gradients for all RTBM units as a flat array. Return type: numpy.array
Theta Diagonal Expectation Unit¶
-
class
theta.layers.DiagExpectationUnitLayer(Nin, Nout, W_init=<theta.initializers.glorot_uniform object>, B_init=<theta.initializers.null object>, Q_init=<theta.initializers.uniform object>, param_bound=16, phase=1)¶ A layer of log-gradient theta units.
Parameters: - Nin (int) – number of inputs.
- Nout (int) – number of outputs.
- W_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for W
- B_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for B
- Q_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for Q
- param_bound (float) – maximum value alowed for the optimization via genetic optimizer.
- phase (complex) – the RTBM phase (default=1)
-
show_activation(N, bound=2)¶ Plots the Nth activation function on [-bound,+bound].
Parameters: - N (int) – the Nth activation function
- bound (float) – min/max value for the plot.
-
get_parameters()¶ Returns: the parameters as a flat array [bh,w,q] Return type: numpy.array
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter of the layer for the GA. Return type: list of numpy.array
-
get_gradients()¶ Returns: B, W and Q gradients as a flat array Return type: numpy.array
-
size()¶ Returns: total number of parameters. Return type: int
Normalized Additive¶
-
class
theta.layers.NormAddLayer(Nin, Nout, W_init=<theta.initializers.null object>, param_bound=10)¶ Linearly combines inputs with outputs normalized by sum of weights. Weights are exponentiated.
\[M(v) = \frac{1}{\sum_{i=1}^N e^{\omega_i}} \sum_{i=1}^{N} e^{\omega_i} P^{(i)}(v)\]Parameters: - Nin (int) – number of input nodes.
- Nout (int) – number of output nodes.
- W_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for weights.
- param_bound (float) – maximum value alowed for the optimization via genetic optimizer.
-
get_parameters()¶ Returns: the parameters as a flat array [w]. Return type: numpy.array
-
get_gradients()¶ Returns: W gradients as a flat array Return type: numpy.array
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter of the layer for the GA. Return type: list of numpy.array
-
size()¶ Returns: total number of parameters. Return type: int
Linear¶
-
class
theta.layers.Linear(Nin, Nout, W_init=<theta.initializers.glorot_uniform object>, B_init=<theta.initializers.null object>, param_bound=10)¶ Linear layer.
Parameters: - Nin (int) – number of inputs.
- Nout (int) – number of outputs.
- W_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for weights.
- B_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for biases.
- param_bound (float) – maximum value alowed for the optimization via genetic optimizer.
-
get_parameters()¶ Returns: the parameters as a flat array [b,w]. Return type: numpy.array
-
get_gradients()¶ Returns: B and W gradients as a flat array Return type: numpy.array
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter of the layer for the GA. Return type: list of numpy.array
-
size()¶ Returns: total number of parameters. Return type: int
Non-Linear¶
-
class
theta.layers.NonLinear(Nin, Nout, activation=<class 'theta.activations.tanh'>, W_init=<theta.initializers.glorot_uniform object>, B_init=<theta.initializers.null object>, param_bound=10)¶ Non-Linear layer.
Parameters: - Nin (int) – number of inputs.
- Nout (int) – number of outputs.
- activation (theta.activations) – the non-linear activation function.
- W_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for weights.
- B_init (theta.initializers) – random initialization for biases.
- param_bound (float) – maximum value alowed for the optimization via genetic optimizer.
-
get_parameters()¶ Returns: the parameters as a flat array [b,w]. Return type: numpy.array
-
get_gradients()¶ Returns: B and W gradients as a flat array Return type: numpy.array
-
get_bounds()¶ Returns: two arrays with min and max of each parameter of the layer for the GA. Return type: list of numpy.array
-
size()¶ Returns: total number of parameters. Return type: int
Minimizers¶
The theta package provides two minimizers:
- CMA-ES (evolutionary strategy)
- Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
We also provide the BFGS optimizer for testing purposes.
Evolutionary algorithm¶
-
class
theta.minimizer.CMA(parallel=False, ncores=0)¶ Implements the GA using CMA-ES library (cma package). This class provides a basic CMA-ES implementation for RTBMs.
Parameters: - parallel (bool) – if set to True the algorithm uses multi-processing.
- ncores (int) – limit the number of cores when
parallel=True.
-
train(cost, model, x_data, y_data=None, tolfun=1e-11, popsize=None, maxiter=None, use_grad=False)¶ Trains the
modelusing the custom cost function.Parameters: - cost (theta.costfunctions) – the cost function.
- model (theta.model.Model or theta.rtbm.RTBM) – the model to be trained.
- x_data (numpy.array) – the support data with shape (Nv, Ndata).
- y_data (numpy.array) – the target prediction.
- tolfun (float) – the maximum tolerance of the cost function fluctuation to stop the minimization.
- popsize (int) – the population size.
- maxiter (int) – the maximum number of iterations.
- use_grad (bool) – if True the gradients for the cost and model are used in the minimization.
Returns: the optimal parameters
Return type: numpy.array
Note
The parameters of the model are changed by this algorithm.
Gradient descent¶
-
class
theta.minimizer.SGD¶ Stochastic gradient descent.
-
train(cost, model, x_data, y_data=None, validation_split=0, validation_x_data=None, validation_y_data=None, stopping=None, scheme=None, maxiter=100, batch_size=0, shuffle=False, lr=0.001, decay=0, momentum=0, nesterov=False, noise=0, cplot=True)¶ Trains the given model with stochastic gradient descent methods
Parameters: - cost (theta.costfunctions) – the cost fuction class
- model (theta.rtbm.Model or theta.model.Model) – the model to be trained
- x_data (numpy.array) – the target data support
- y_data (numpy.array) – the target data prediction
- validation_split (float) – fraction of data used for validation only
- validation_x_data (numpy.array) – external set of validation support
- validation_y_data (numpy.array) – external set of validation target
- stopping (theta.stopping) – the stopping class (see
theta.stopping) - scheme (theta.gradientscheme) – the SGD method (Ada, RMSprop, see Gradient descent schemes)
- maxiter (int) – maximum number of allowed iterations
- batch_size (int) – the batch size
- shuffle (bool) – shuffle the data on each iteration
- lr (float) – learning rate
- decay (float) – learning rate decay rate
- momentum (float) – add momentum
- nesterov (bool) – add nesterov momentum
- noise (bool) – add gaussian noise
- cplot (bool) – if True shows the cost function evolution
Returns: iterations, cost and validation functions
Return type: dictionary
Note
The parameters of the model are changed by this algorithm.
-
-
class
theta.minimizer.BFGS¶ Implements the BFGS method
-
train(cost, model, x_data, y_data=None, tolfun=1e-11, maxiter=100)¶ Parameters: - cost (theta.costfunctions) – the cost function.
- model (theta.model.Model or theta.rtbm.RTBM) – the model to be trained.
- x_data (numpy.array) – the support data with shape (Nv, Ndata).
- y_data (numpy.array) – the target prediction.
- tolfun (float) – the maximum tolerance of the cost function fluctuation to stop the minimization.
- popsize (int) – the population size.
- maxiter (int) – the maximum number of iterations.
Returns: the optimal parameters
Return type: numpy.array
Note
The parameters of the model are changed by this algorithm.
-
Gradient descent schemes¶
-
class
theta.gradientschemes.adagrad(epsilon=1e-05)¶ The Adagrad scheme.
Parameters: epsilon (float) – smoothing term to avoid division by zero -
getupdate(G, lr)¶ Get updates.
Parameters: - G (numpy.array) – gradients
- lr (float) – learning rate
Returns: the updated gradient.
Return type: numpy.array
-
-
class
theta.gradientschemes.RMSprop(rate=0.9, epsilon=1e-05)¶ The RMS propagation scheme.
Parameters: - rate (float) – weighting of the previous squared gradient expectation value
- epsilon (float) – smoothing term to avoid division by zero
-
getupdate(G, lr)¶ Get updates.
Parameters: - G (numpy.array) – gradients
- lr (float) – learning rate
Returns: the updated gradient.
Return type: numpy.array
-
class
theta.gradientschemes.adadelta(rate=0.9, epsilon=1e-05)¶ The Adadelta scheme.
Parameters: - rate (float) – weighting of the previous squared gradient expectation value
- epsilon (float) – smoothing term to avoid division by zero
-
getupdate(G, lr)¶ Get updates.
Parameters: - G (numpy.array) – gradients
- lr (float) – learning rate
Returns: the updated gradient.
Return type: numpy.array
-
class
theta.gradientschemes.adam(b1=0.9, b2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08)¶ The Adam scheme.
Parameters: - b1 (float) – weight of the previous first moment of the gradient estimate
- b2 (float) – weight of the previous second moment of the gradient estimate
- epsilon (float) – smoothing term to avoid division by zero
-
getupdate(G, lr)¶ Get updates.
Parameters: - G (numpy.array) – gradients
- lr (float) – learning rate
Returns: the updated gradient.
Return type: numpy.array
Activations¶
All activations functions are inherited from the
theta.activations.actfunc class, so custom activations can be
implemented by extending that class.
The current code contains the following activation functions:
Linear¶
-
class
theta.activations.linear¶ A linear pass through.
-
static
activation(x)¶ Evaluates the activation function.
Parameters: x (numpy.array) – the input data. Returns: the activation function evaluation. Return type: numpy.array
-
static
gradient(x)¶ Evaluates the gradient of the activation function.
Parameters: x (numpy.array) – the input data. Returns: the gradient of the activation function. Return type: numpy.array
-
static
Sigmoid¶
-
class
theta.activations.sigmoid¶ The sigmoid activation.
-
static
activation(x)¶ Evaluates the activation function.
Parameters: x (numpy.array) – the input data. Returns: the activation function evaluation. Return type: numpy.array
-
static
gradient(x)¶ Evaluates the gradient of the activation function.
Parameters: x (numpy.array) – the input data. Returns: the gradient of the activation function. Return type: numpy.array
-
static
Tanh¶
-
class
theta.activations.tanh¶ The tanh activation.
-
static
activation(x)¶ Evaluates the activation function.
Parameters: x (numpy.array) – the input data. Returns: the activation function evaluation. Return type: numpy.array
-
static
gradient(x)¶ Evaluates the gradient of the activation function.
Parameters: x (numpy.array) – the input data. Returns: the gradient of the activation function. Return type: numpy.array
-
static
Custom activation functions can be implemented by extending the theta.activations.actfunc class.
Initializers¶
All initializers are inherited from the
theta.initializers.initializer class, so custom initializers can
be implemented by extending that class.
The current code contains the following parameter initalizers:
Uniform¶
-
class
theta.initializers.uniform(bound=1, center=0)¶ Uniformly distributed initialization.
Parameters: - bound (float) – half-width of the distribution [-bound,+bound]
- center (float) – location of the center
Cost functions¶
All cost functions are inherited from the
theta.costfunctions.costfunction class, so custom costs can be
implemented by extending that class.
The current code contains the following cost functions:
Stopping conditions¶
The stopping condition can be used with the theta.minimizer.SGD
minimizer. The validation data is monitored and if a specific
condition is achieved the optimization is stopped. Custom stopping
conditions can be implemented by extending the
theta.minimizer.stopping abstract class.
The current code contains the following stopping algorithms:
Early Stop¶
-
class
theta.stopping.earlystop(delta=10)¶ A simple implementation of early stopping. If the validation loss function increases after delta iterations the stop signal is send to the minimizer.
Parameters: delta (int) – the number of iterations to pass until the stopping condition check becomes active. -
do_stop(v)¶ Function which tests if the stop condition is reached.
Parameters: v (numpy.array) – history of the validation loss function. Returns: True if the validation loss is growing in the delta window, False elsewhere. Return type: bool
-